Peer-reviewed by Dr. Gabriel Krenitsky, MD and Anthony Castore, SSRP Fellow
Step into the world of peptides, where science meets biology to transform how we treat, repair, and optimize the human body. Peptides are short chains of amino acids, typically consisting of 2 to 50 amino acids, and are the building blocks of proteins. They play crucial roles in various biological functions within the body. The science behind peptides lies in their ability to act as signaling molecules, influencing how cells behave and regulating biological processes. Peptides occur naturally in the body and are involved in functions such as cell signaling, immune responses, and hormone regulation.
In medical and fitness contexts, synthetic peptides mimic natural peptides. For instance, growth hormone-releasing peptides (GHRPs) stimulate growth hormone production, enhancing muscle recovery, improving skin elasticity, and supporting fat loss. Other peptides, like BPC-157, are used for tissue repair and healing.
In 2024, peptides are now at the forefront of medicine, biotechnology, and fitness, offering revolutionary solutions for challenges ranging from aging and disease to performance enhancement. These tiny molecules reshape how we think about health by mimicking the body’s natural processes to:
- Regenerate tissue
- Boost muscle growth
- Enhance cognitive function
- Combat chronic illnesses
What sets peptides apart is their dual identity—they’re both naturally derived and scientifically engineered. This makes them safer and more targeted than many traditional therapies, opening doors to personalized health solutions that align seamlessly with the body’s biology. However, like any intervention, there are critical factors to understand before starting a peptide regimen.

Anthony Castore, SSRP Fellow, at the Peptide Conference – Photo by Drew Shaffer Photography
A Complex Approach to Clinical Integration: The Science Behind Peptides
Peptides are precise biological tools designed to interact with specific cellular receptors and regulate vital physiological processes such as tissue repair, hormonal balance, and immune responses. Their structural versatility and targeted mechanisms of action make them indispensable in advancing clinical therapies.
Incorporating peptides into clinical practice demands a nuanced understanding of their molecular specificity. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals, peptides require precise dosing, receptor-specific targeting, and careful monitoring to maximize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing potential risks. Their integration represents a sophisticated approach to personalized medicine, enabling clinicians to address complex health challenges with unparalleled accuracy.
Key Considerations for Clinical Integration
- Structure and Function
- Peptides are smaller than proteins, allowing easier cellular entry and influence over biological activity.
- Their function is determined by the sequence of amino acids, dictating roles like hormone regulation, immune responses, tissue repair, and metabolism.
- Types of Peptides
- Signaling Peptides: Messenger molecules that trigger cellular responses (e.g., insulin regulates blood sugar).
- Antimicrobial Peptides: Strengthen immunity by disrupting pathogen membranes.
- Growth Factors: Promote cell regeneration for tissue repair (e.g., collagen peptides).
- Peptides and Cell Receptors
- Peptides bind to specific receptors, activating or inhibiting cellular functions.
- These interactions initiate biological responses, such as gene expression, protein synthesis, or enzyme activation.
- Therapeutic Uses
- Medical: Treat diabetes, cancer, and neurological diseases.
- Cosmetic: Promote skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles.
- Sports Medicine: Aid in muscle recovery and tissue repair.
- Synthetic Peptides
- Lab-engineered peptides target specific conditions, offering precise therapeutic solutions.
- Absorption and Bioavailability
- Delivery methods (injections, topical creams, or oral supplements) impact absorption, as oral peptides can degrade in digestion.
- Potential in Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine
- Peptides like GHRPs stimulate growth hormone production, potentially improving muscle mass, skin health, and overall vitality.

Selecting the Right Peptide
Choosing the correct peptide is like selecting the perfect tool for a highly specific task—it requires precision, understanding, and alignment with your unique goals. With peptides offering benefits ranging from muscle repair and fat loss to enhanced cognitive performance and anti-aging effects, selecting the right one means delving into the science behind their functions and your body’s needs. The key lies in knowing your objectives: Are you seeking faster recovery, a boost in metabolism, or skin that radiates youth? Pairing these goals with the appropriate peptide—and ensuring quality, purity, and professional guidance—unlocks their true potential. In a world where the wrong choice can mean missed results, selecting the suitable peptide is both an art and a science, making every step of the process vital for success.
Different peptides serve different purposes, so understanding which peptide aligns with your goals is vital. For example, peptides like TB-500 and BPC-157 are primarily used for recovery and healing, while Ipamorelin or CJC-1295 are favored for their muscle-building and anti-aging effects. Choosing the wrong peptide for your specific needs could not only yield poor results but also increase the risk of unwanted side effects.
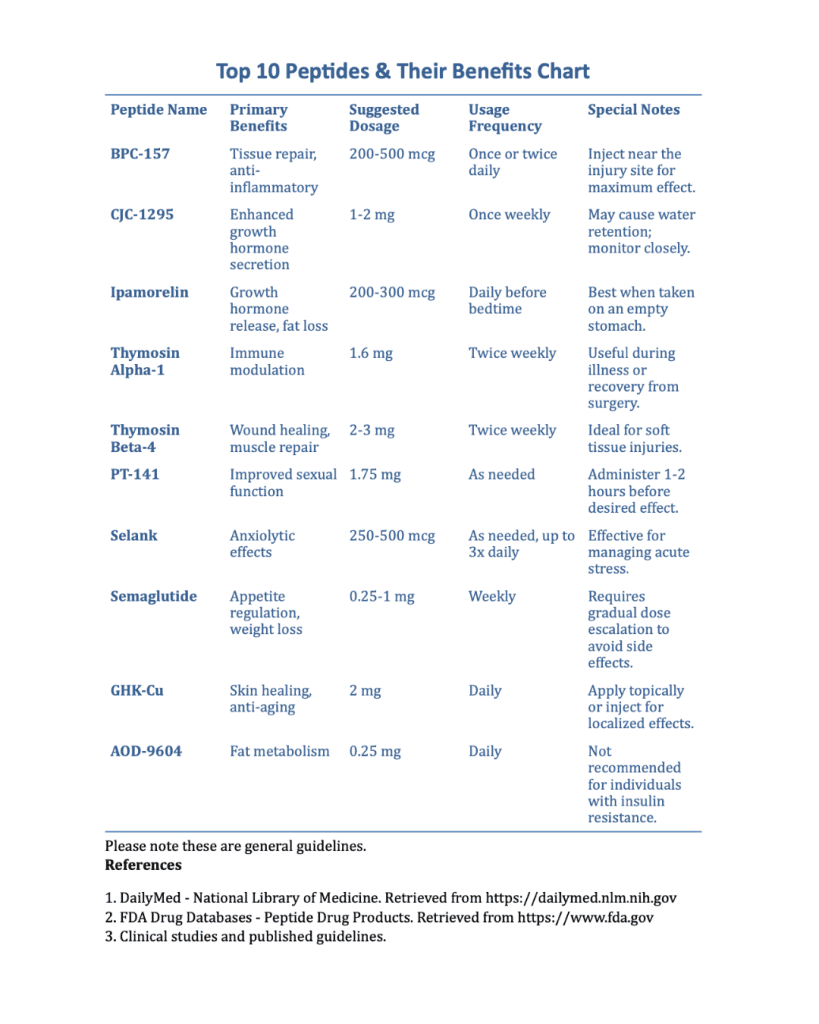
Dosage and Administration
One of the most important aspects of peptide use is getting the dosage and administration protocol correct. Peptides are typically administered via subcutaneous injections, though some may come in oral or topical forms. The dosage will depend on factors such as your body weight, goals, and overall health. Over- or under-dosing can result in ineffective results or adverse reactions. Sticking to the recommended dosage and administration frequency, usually as directed by a healthcare professional, is essential to maximizing benefits while minimizing risks. Compounding pharmacies will often provide dosing instructions for the peptides they supply.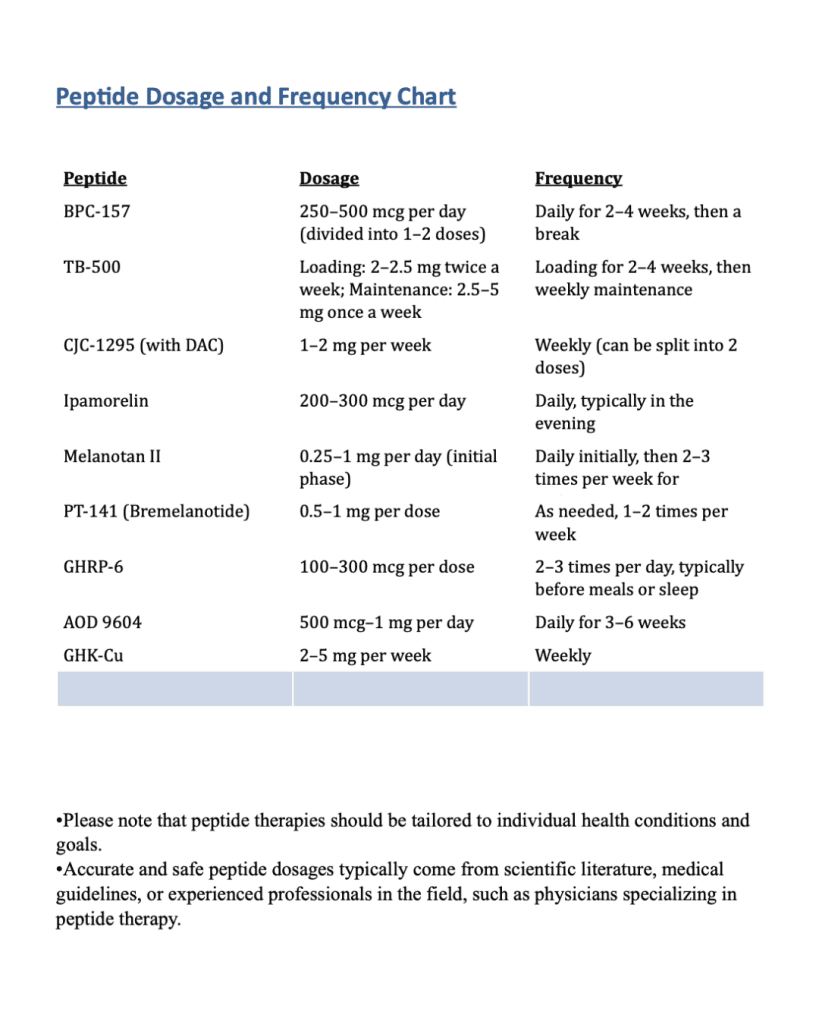
Quality and Sourcing
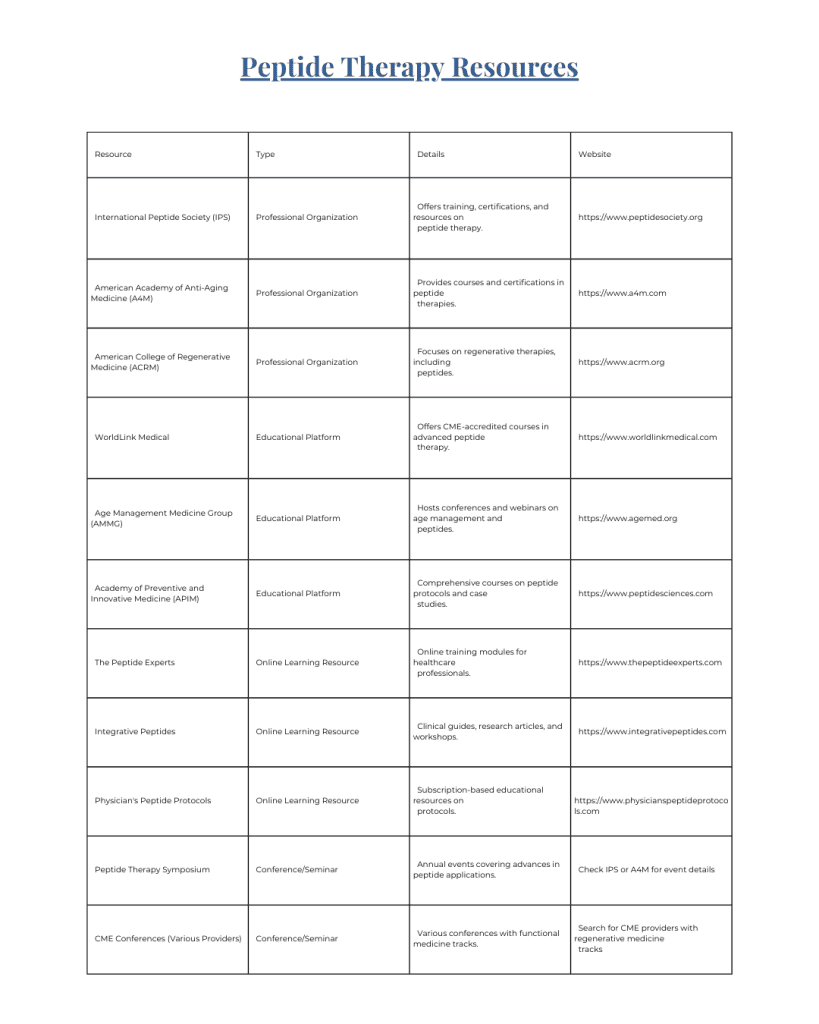
Peptides must be of high quality to ensure safety and effectiveness. Avoid ordering from unverified online sources, as many products may be counterfeit, contaminated, or improperly stored, leading to poor results or health risks. Refer to the Licensed Medical Professional Reference Chart to find trusted providers if you’re interested in using peptides. Always prioritize safety and legitimacy.
Understanding Potential Side Effects
While peptides are generally considered safe when used properly, they are not without potential side effects. Common side effects include water retention, joint stiffness, fatigue, and localized reactions at injection sites. More serious side effects, such as hormone imbalances or immune system disruptions, can occur if peptides are misused. It’s essential to closely monitor how your body reacts to peptides and seek medical advice if you experience unusual symptoms.
Legal Considerations
Peptide usage is governed by different legal frameworks depending on where you live. Certain peptides are classified as controlled substances in some countries and are only available via prescription. For athletes, the use of specific peptides may be prohibited by anti-doping agencies, so it’s essential to be aware of the legalities before starting therapy, especially if you compete in sports.
The science behind peptides is growing rapidly but fundamentally revolves around their ability to act as key regulators of biological processes. Peptides influence growth, repair, immune responses, and metabolic functions via unique interactions with cell receptors. Their versatility and effectiveness make them highly valuable in both medical and cosmetic applications. Additionally, their utilization is rapidly becoming part of cutting-edge medical practices focusing on the holistic approach to medical treatments.
There is a wealth of information for healthcare providers looking to incorporate peptides into their medical practice. It is important to consult your physician for those considering beginning peptide therapy.






0 Comments